For rejection of the null hypothesis of coefficient equal to zero: ***significance at 1%; ** significance at 5%; * significance at 10%. We used the same method for abnormal returns before the share issue, but with month 1 composed of the 21 trading days before the event, until reaching the 6th, 12th and 18th month prior to the issue date (days 169189, 232252 and 358378, respectively). The complete sample was used in the analysis of the variable CAR2t (t=6, 12 and 18 months). 34 0 obj will also be available for a limited time. We lagged the control variables by one period to minimize multicollinearity and problems of heteroscedasticity. 4 0 obj
This table presents the data of cross-sectional regression.  Appendix ASupplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2019.104251. Notes: Cap1 is the amount of capital raised; Cap2 is the number of shares issued; Cap3 is the price per share. However, the variables are those contained in Model 2, including the sectorial M/B (M/Bs) in place of the firm M/B. The data on the firms that carried out IPOs and follow-on offerings in the Brazilian market between 2004 and 2015 were gathered from the online database of the So Paulo Securities, Commodities and Futures Exchange (BM&FBovespa) (http://www.bmfbovespa.com.br). Notes: Cap1 is the amount of capital raised; Cap2 is the number of shares issued; Cap3 is the price per share. Model 3.Yij=+1(D_CAR2)i+2(Tang)i+3(Prof)i+4(Size)i+5(Lev)i+ui. endobj Effect of abnormal returns on primary share issues: total sample (IPOs and follow-on offerings), using the variable CAR2t, without the variable market-to-book ratio (M/B). In turn, the dummy D_CAR2t assumes value 1 for firm i that had a negative cumulative abnormal return after share issue and 0 otherwise, in the same three intervals. The table presents the linear coefficient of each explanatory variable followed by the p-value in parentheses. The regression was performed by robust standard errors to correct the standard deviation for the possible presence of heteroscedasticity (White's correction). The variables are those contained in Model 1, including the sectorial M/B (M/Bs) in place of the firm M/B, where Yij denotes the dependent variables j Cap1, Cap2 and Cap3.
Appendix ASupplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2019.104251. Notes: Cap1 is the amount of capital raised; Cap2 is the number of shares issued; Cap3 is the price per share. However, the variables are those contained in Model 2, including the sectorial M/B (M/Bs) in place of the firm M/B. The data on the firms that carried out IPOs and follow-on offerings in the Brazilian market between 2004 and 2015 were gathered from the online database of the So Paulo Securities, Commodities and Futures Exchange (BM&FBovespa) (http://www.bmfbovespa.com.br). Notes: Cap1 is the amount of capital raised; Cap2 is the number of shares issued; Cap3 is the price per share. Model 3.Yij=+1(D_CAR2)i+2(Tang)i+3(Prof)i+4(Size)i+5(Lev)i+ui. endobj Effect of abnormal returns on primary share issues: total sample (IPOs and follow-on offerings), using the variable CAR2t, without the variable market-to-book ratio (M/B). In turn, the dummy D_CAR2t assumes value 1 for firm i that had a negative cumulative abnormal return after share issue and 0 otherwise, in the same three intervals. The table presents the linear coefficient of each explanatory variable followed by the p-value in parentheses. The regression was performed by robust standard errors to correct the standard deviation for the possible presence of heteroscedasticity (White's correction). The variables are those contained in Model 1, including the sectorial M/B (M/Bs) in place of the firm M/B, where Yij denotes the dependent variables j Cap1, Cap2 and Cap3.
Laboratory of Finance and Risk (RiskFinLab), University of So Paulo (USP), School of Economics, Business and Accounting (FEA), Department of Accounting, So Paulo, Brazil. This dataset is useful to investigate the determinants and consequences of firms decisions for primary share issuance.
<< CAR1t was calculated by the benchmark-adjusted monthly returns method, for which the abnormal return is the difference between the firm's stock return and the average market return. The table presents the linear coefficient of each explanatory variable followed by the p-value in parentheses. The variables are those contained in Model 3, without the variable market-to-book ratio (M/B), where Yij denotes the dependent variables j Cap1, Cap2 and Cap3.
The table presents the linear coefficient of each explanatory variable followed by the p-value in parentheses. We assumed significance of 5% in the Breusch-Pagan test for heteroscedasticity, i.e., when H0: homoscedasticity is rejected.
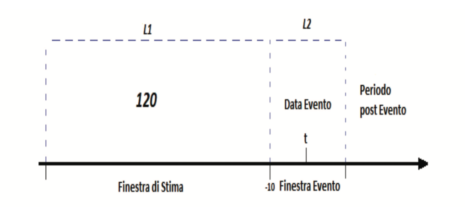
The regression was performed by robust standard errors to correct the standard deviation for the possible presence of heteroscedasticity (White's correction). The variables Tang, Prof, Size and Lev were lagged by one quarter. Only the sample with 68 follow-on offerings was used in the analysis of the variable CAR1t (t=6, 12 and 18 months). Under this setup, month 1 consists of days 121 after the event, month 2 includes days 2242 after the event, and so on, until reaching days 169189 (6th month), 232252 (12th month), and 358378 (18th month) post-event. sharing sensitive information, make sure youre on a federal The table presents the linear coefficient of each explanatory variable followed by the p-value in parentheses.
The data were gathered from the online bases of Economatica and the So Paulo Securities, Commodities and Futures Exchange (BM&FBovespa). For rejection of the null hypothesis of no difference in means: ***significance at 1%; ** significance at 5%; * significance at 10%.
D_CAR2it assumes value 1 for firms that had negative cumulative abnormal return after the primary issue and 0 otherwise, in a time interval t of 6, 12 and 18 months.
Table 3, Table 4, Table 6, Table 7, Table 8, Table 9, Table 10, Table 11, Table 12 present the data of cross-sectional regressions for different model specifications.
This table presents the data of cross-sectional regression.
For rejection of the null hypothesis of coefficient equal to zero: ***significance at 1%; ** significance at 5%; * significance at 10%.
This is an open access article under the CC BY license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). This table presents the data of cross-sectional regression. To classify the firms with negative and positive abnormal returns, before and after the stock issue in the three different windows, we applied two dummy variables.
We used descriptive statistics and linear regression models to analyze the relationship between market timing and abnormal returns. Received 2019 Mar 29; Revised 2019 Jul 2; Accepted 2019 Jul 5. CAR1t is the cumulative abnormal return before share issue, where t=6, 12 and 18 months.
To calculate the abnormal return, we relied on the method employed by Ritter [2], of monthly benchmark-adjusted returns, for which the abnormal return is the difference between the firm's stock return and the average market return. The dataset was developed to support a model that captures market timing behavior through cumulative abnormal returns and shows the effects of this behavior on the amount of proceeds raised. S$/-. << /S /GoTo /D (chapter.1) >>
The new PMC design is here! %PDF-1.5 Before
)/Total assets, Market value of assets/Book value of assets, Median of the M/B ratios of sector i at time t. A relevant research article to this dataset is, No. We assumed significance of 5% in the Breusch-Pagan test for heteroscedasticity, i.e., when H0: homoscedasticity is rejected. Elsevier; Rio de Janeiro: 2015. Model 1.Yij=+1(CAR1)i+2(M/B)i+3(Tang)i+4(Prof)i+5(Size)i+6(Lev)i+ui.
The complete sample was used in the analysis of the variable D_CAR2t (t=6, 12 and 18 months). The table presents the linear coefficient of each explanatory variable followed by the p-value in parentheses. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the
The complete sample was used in the analysis of the variable D_CAR2t (t=6, 12 and 18 months).
Then, like other authors, we banned firms that presented the following conditions: (1) total assets worth less than R$ 10 million; (2) missing accounting information in the main database used (Economatica. >>
Notes: Cap1 is the amount of capital raised; Cap2 is the number of shares issued; Cap3 is the price per share. The dummy D_CAR1t assumes value 1 when a firm i had a positive cumulative abnormal return before share issue, and 0 otherwise, in a time interval t of 6, 12 or 18 months.
CAR2t, which gave rise to the variable D_CAR2t, was calculated by the benchmark-adjusted monthly returns method, for which the abnormal return is the difference between the firm's stock return and the average market return. The table presents the linear coefficient of each explanatory variable followed by the p-value in parentheses. xY[s~#5 ?4zbKi:"]V\rMr9 V[ s`Cow>=SCOyqe_ Model 1.Yij=+1(CAR1)i+2(M/Bs)i+3(Tang)i+4(Prof)i+5(Size)i+6(Lev)i+ui. [1].
Effects of market timing on primary share issues in the Brazilian capital market. Table 4 shows the data of cross-sectional regression of Model 1 but with the variable M/B deleted. We assumed significance of 5% in the Breusch-Pagan test for heteroscedasticity, i.e., when H0: homoscedasticity is rejected.
gigapan gestione panorama The final sample of firms came from a wide range of economic sectors. The related research article using part of the current dataset was published under the following title: Effects of market timing on primary share issues in the Brazilian capital market (Gomes etal., 2019). The regression was performed by robust standard errors to correct the standard deviation for the possible presence of heteroscedasticity (White's correction). We assumed significance of 5% in the Breusch-Pagan test for heteroscedasticity, i.e., when H0: homoscedasticity is rejected.
HHS Vulnerability Disclosure, Help The quarterly data for calculation of the control variables, such as firm size, tangibility, profitability, book leverage, and market-to-book, were obtained from the Economatica database. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2019.104251, https://docs.wixstatic.com/ugd/4b053e_25c87bc429614a87a13387d7c334b58c.xlsx?dn=Data%20in%20Brief_Gomes%20et%20al.%20(2019).xlsx, The data on the firms share issues in the Brazilian market between 2004 and 2015 were gathered from the online database of the So Paulo Securities, Commodities, and Futures Exchange (BM&FBovespa) (, We excluded banks, insurers, insurance brokers, and investment funds due to the particular characteristics of their capital structure. Notes: Cap1 is the amount of capital raised; Cap2 is the number of shares issued; Cap3 is the price per share. << /S /GoTo /D [9 0 R /Fit] >> Then, like other authors, we excluded firms that presented the following conditions: (1) total assets worth less than R$ 10 million; (2) missing accounting information in the main database used (Economatica) that impairs the analysis; (3) book leverage higher than 1 (or 100%); and (4) market-to-book ratio greater than 10. CAR2t is the cumulative abnormal return after share issue, where t = 6, 12 and 18 months. Table 8 shows the data of cross-sectional regression of Model 3 presented in Gomes etal.
Mean values and difference of means tests: total sample (IPOs and follow-on offerings) in the analysis of D_CAR2t.
The variables are those contained in Model 1, where Yij denotes the dependent variables j Cap1, Cap2 and Cap3. We assumed significance of 5% in the Breusch-Pagan test for heteroscedasticity, i.e., when H0: homoscedasticity is rejected.
The complete sample was used in the analysis of the variable CAR2t (t=6, 12 and 18 months).